June 12, 2020 ( last updated : June 12, 2020 )
Search
Brute Force
Backtracking
DFS
Branch and Bound
BFS
Data Structure and Algorithm
https://github.com/cao-weiwei/
Brute Force Searching strategy is a useful problem-solving approach that systematically enumerates all possible candidates for the solution and then selecting the proper candidates as the result set.
Introduction
It is usually used to search all possible results for a specific problem, and if there are overlapping subproblems, Greedy or Dynamic Programming skills can be applied based on the brute force process to get optimal solutions.
Backtracking and Branch and Bound are two strategies for applying the Brute Force Searching approach to find all the solutions. Those two methods are also as known as DFS and BFS strategy separately.
Before we dive into more details of them, let’s familiar with two useful techniques for utilizing those strategies. The first thing is called State Space Tree, which can represent all possible solutions using a tree structure in which successive states of an instance are considered. The second is Bounding Function, it is nothing but conditions to terminate invalid nodes in the tree so that the desired candidates are selected for goals and killing unnecessary branches of the tree to save time.
Backtracking
The logic of Backtracking is that searching from the root of a state space tree to get all the promising leaves which are the results meeting the constrains.
-
Firstly, take one element from the given pool, and
-
Then, checking the bounding function (conditions) to see if current exploration can go further.
-
If OK, then take one of the remaining elements from the pool to generate an intermediate result, and then repeat #2, until reaching the end of the tree.
-
After traversing this leaf, we need to go back to the previous step, so we should remove this point added to the result.
Below is an example of applying backtracking method to get all possible results.
![]()
As the above figure showing, the state space tree displays how Backtracking method working and obvious it’s a type of DFS strategy and using bounding function to prune the tree.
-
DFS:pre-orderoccurs when making choice from pool to select an element, andpost-orderoccurs when revoking the choice. -
Pruning state space tree to avoid useless searching before
pre-orderoperation and adding current path into the result set.
The Backtracking can be broken down into following two parts in pseudocode
def backtrack(current_path, depth, pool):
# 0. base case
if depth reaches the bottom:
if current_path is a promising path:
solutions.append(current_path)
return
# 1. visiting all nodes in state space tree
for element in pool:
if element is not a valid choice: continue
else:
current_path.append(element) # make choice
backtrack(current_path, depth + 1, pool) # go to next depth
current_path.pop(element) # move back, cancelling the choice
The difference between traditional DFS and the above pseudocode is that how to avoid visiting elements that have been searched. Actually, the way how an element is selected from the pool and the validation of the currently selected element can complete such a thing. Here are some exercises for this pattern🤓
- Permutation
- Combination
- DFS
Branch and bound
Another strategy using brute force searching is Branch and Bound, which follows BFS pattern to find [all possible] candidates of the solution. The logic is similar with BFS, we start from the root of state space tree and put that element into a queue to generate next level nodes and exploring breadthwise. The following figure shows an instance that how BFS works to get the answer.
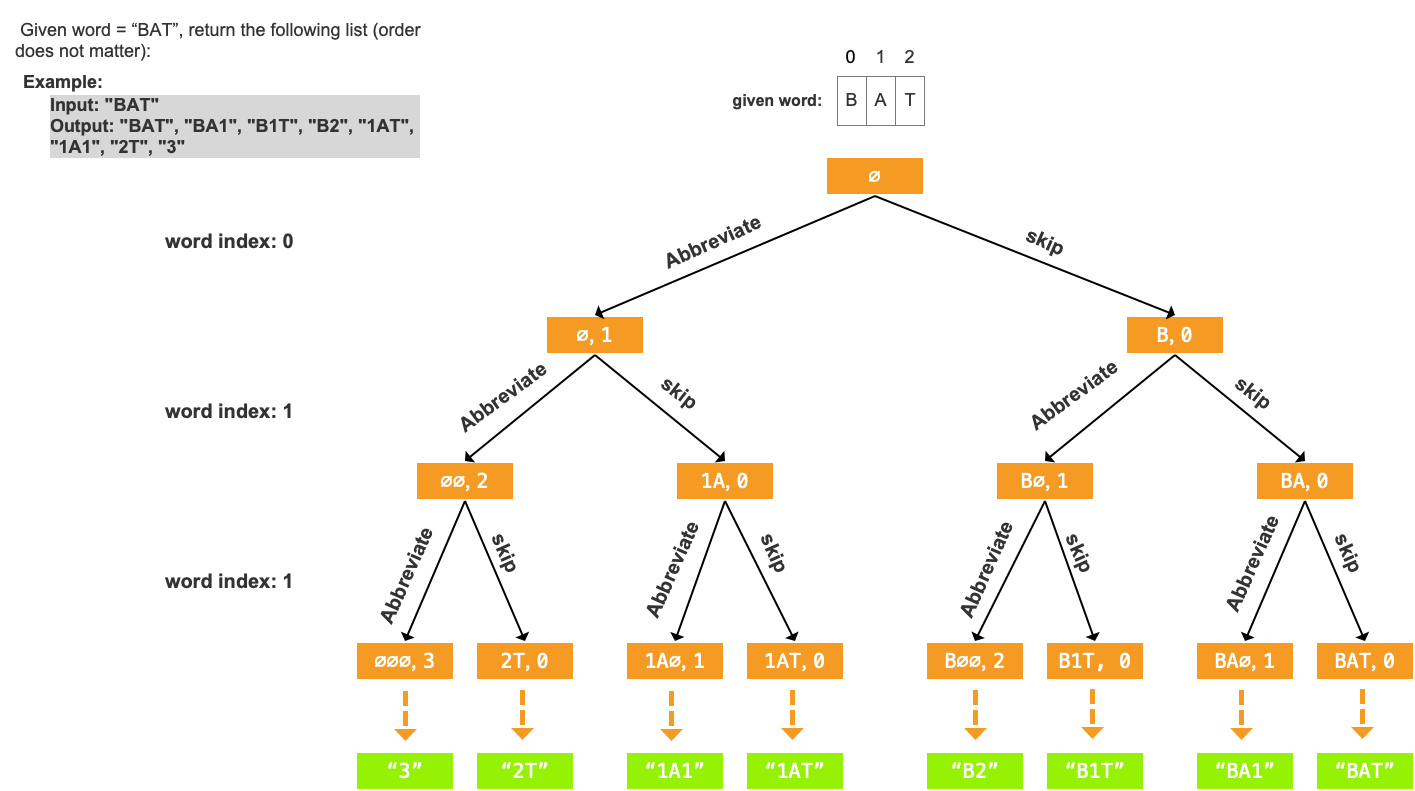
This method is often used to find a possible shortest path, and what modifications are needed is the bounding functions. If you want to assess your understanding, please check this👉:
If you like my articles please give me a star or leave comments below, thanks!
Originally published June 12, 2020
Latest update June 12, 2020
Related posts :